Lead smelting and lead alloy classification Asian Metal
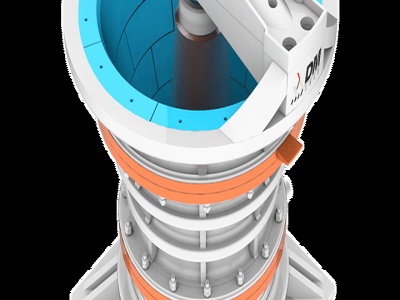
It also requires two chemical reactions to occur within the furnace. 1) Due to the sulfur content, carbon from the coke will not be able to reduce lead. Therefore, the mineral must be roasted to oxidize sulfur and create a metal oxide out of galena. 2) Raw ore is then added to the products and is heated further.